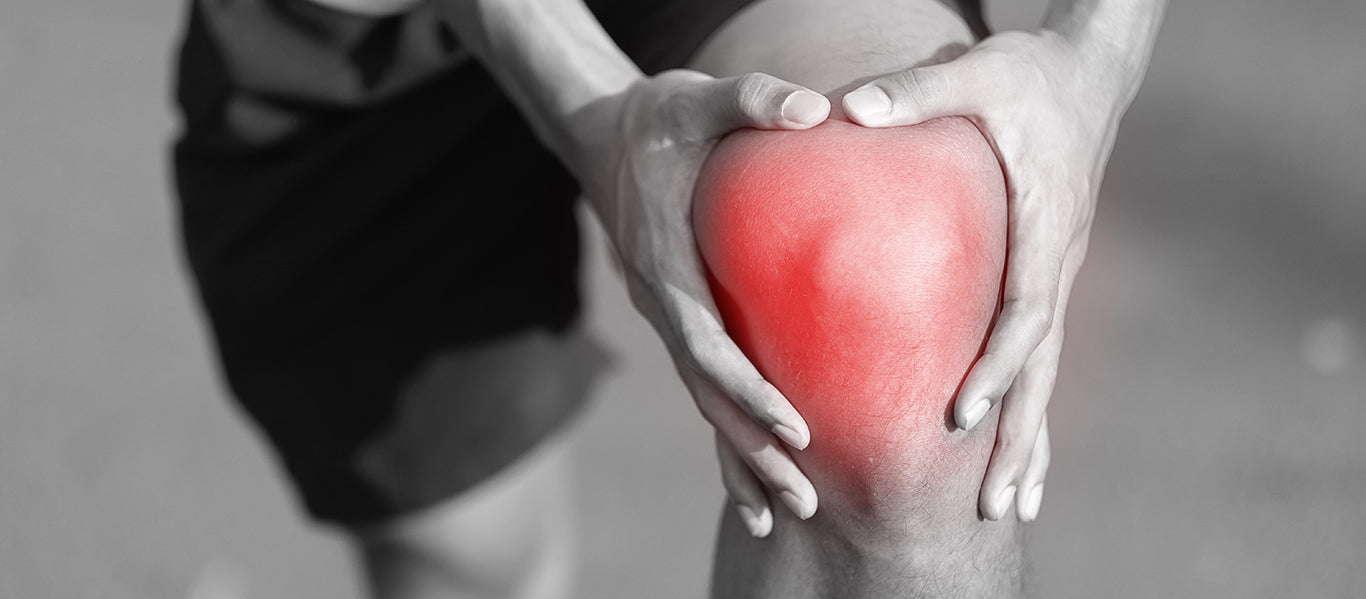
Soft tissue injuries are the most typical injuries resulting from engagement in sport.
They consist of the following:
- skin injuries-- abrasions, lacerations and also blisters
- muscular tissue injuries-- splints or stress of muscle mass fibers and also contusions
- tendon injuries-- splints or stress of ligament fibers and also inflammation (tendonitis).
- ligament injuries-- strains and splits of tendon fibers.
Soft-tissue injuries can result in inner blood loss as well as swelling. Prompt and efficient management of this blood loss helps recovery.
Tears, sprains, and contusions.
A tear is a disruption of the fibers of a muscle or tendon. This can be small and also microscopic (typically called a strain). A tear can also be more extreme, and entail bigger fibers of muscular tissues as well as ligaments. Splits (as well as stress) take place when a muscular tissue or ligament is overstretched or when a muscle agreements too quickly. The seriousness of the tear can range from the tiny level (stress) to a handful of fibers via a full rupture of all muscle mass fibers.
A strain is a tear of tendon fibers, muscular tissues, or tendons sustaining a joint. This can happen when a joint is extended beyond its typical range of motion. A strain can entail a handful of fibers through to a full rupture. In extreme circumstances, the fibers of the tendon, muscle, or tendon can stay intact and slit from the bone.
A contusion or contusion is hemorrhaging right into the soft cells. It is caused by a direct impact from another person, an application, or a thing. Swelling can occur to any kind of soft cells of the body.
Skin abrasions, lacerations, and sores Injuries to the skin are really typical in sporting activity. They consist of minor injuries, such as abrasions (grazes), blisters, and also tiny lacerations. They additionally include bone cracks and more significant lacerations that require suturing (stitches). Tiny skin abrasions, lacerations not requiring sutures, and sores are workable conditions, and for the most part, do not require a referral to a doctor. Skin abrasions happen when the external layer of skin is gotten rid of, typically as a result of a scratching activity. The open wound can contain dust or crushed rock, which ought to be removed. More comprehensive, deeper abrasions require medical interest.
When the skin is lacerated (cut), the depth, as well as the location of the laceration, will certainly establish whether suturing is needed. Medical interest is needed if the laceration is deep sufficient to subject cells, such as fat, ligaments, or bone. Often a superficial laceration will certainly require suturing. This can be called for if the laceration is located.
- over a joint (such as the knee) because flexion will consistently open up the wound.
- in a cosmetically sensitive position (as an example, on the face).
Deep lacerations are generally accompanied by considerable blood loss.
Sores result from friction (rubbing). One layer of skin separates from an additional and also a small pocket of fluid forms.
Blisters can be brought on by devices, shoes, pressure from callus accumulation, increased training loads, or merely by the recommencement of training after an extended pause.
The first phase of repair of body tissue is the severe inflammatory stage. It exists throughout the first 24 to 72 hrs after injury. The instant feedback of the body to injury is to boost the circulation of blood and also other liquids to the hurt site. If blood vessels at the site are damaged there will certainly also be direct blood loss into the bordering cells. The build-up of liquid in the area triggers a rise in tissue pressure, which creates pain.
All these adjustments generate what we call inflammation. Swelling contains inflammation, warmth, swelling, pain as well as the loss of function. If inflammation is left unchecked and continues for a long period of time, the development of mark tissue will be extra extreme.
The extent to which the development of stringent scar tissue can be stopped will, in part, establish.
The time needed for rehabilitation of the injury and also the degree to which normal functioning can be returned to pre-injury levels shows how stretching and the application of ice will restrict the formation of scar cells.
411 on soft-tissue injuries! Part 1